Introduction to DCP Fire Extinguisher
A DCP fire extinguisher is a dry chemical powder. A fire extinguisher is one of the most widely used fire safety devices in buildings, homes, factories, and cars.
It operates by emitting a fine powder that rapidly smothers the fire and breaks the chemical reaction of fire.
The fire extinguisher is particularly effective in combating Class A, Class B, and Class C fires.
The most important features of these extinguishers are their immediate availability and the fact that they can be used by one or two people only.
What is a fire extinguisher?
A DCP extinguisher consists of a cylinder of finely powdered chemicals that are expelled by means of an inert gas contained either in a compressed gas cartridge located within the DCP cylinder, as in the case of portable extinguishers, or stored in a separate cylinder tied outside the DCP cylinder, as in the case of a trolley-mounted extinguisher.
A fire extinguisher is a portable device used to extinguish small fires before they spread. Fire extinguishers are usually color-coded red in cylinders. They are designed for quick response in emergencies.
Expand Your Knowledge on [Fire extinguisher type]
Importance of DCP in Fire Safety
The DCP fire extinguisher is also known as a universal fire extinguisher. This extinguisher is used for multiple purposes.
This extinguisher powder is nonconductive, so it can be used in electrical fires, but hitting the DCP extinguisher on electrical equipment can damage the electrical circuit.
DCP extinguishers are easily available in different sizes, easy to operate, and affordable.
Indian Standard—2171
Color code: blue bend
What is a DCP fire extinguisher?
A DCP fire extinguisher is a dry chemical powder fire extinguisher. This type of fire extinguisher is used in Class A, B, and C fires.
Full Form and Meaning of DCP
Dry chemical powder
DCP fire extinguisher powder names are
Dry chemical powder is a non-conductive powder made from various chemical compounds.
- Monoammonium phosphate (MAP)
- Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃)
- Potassium bicarbonate (KHCO₃)
- Urea-based potassium bicarbonate
| Compound | Fire class | Color code | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monoammonium phosphate | A, B, C | Yellow | ABC fire |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | B, C | White | kitchen, vehicles |
| Potassium Bicarbonate | B, C | Purple | Oil & gas industries |
| Urea-based Bicarbonate | B, C | White | Specialized extinguishers |
Role of Propellant Gas (CO₂ or Nitrogen)
The propellant gas used shall be carbon dioxide or nitrogen. The maximum quantity of propellant gas to be used for various capacities of DCP extinguishers shall be such that the internal pressure of the DCP cylinder shall at no point in time exceed 15 kg/cm².
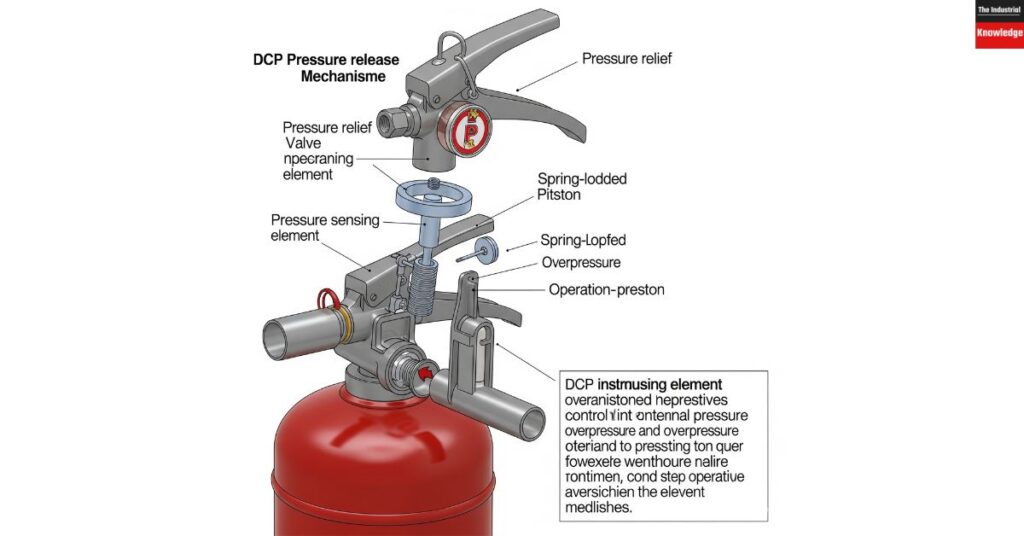
Pressure release mechanism
Classes of Fire and DCP Applicability
4.1 Class A – Ordinary Combustibles
4.2 Class B – Flammable Liquids
4.3 Class C – Flammable Gases
4.4 Unsuitable Classes (Class D, K)
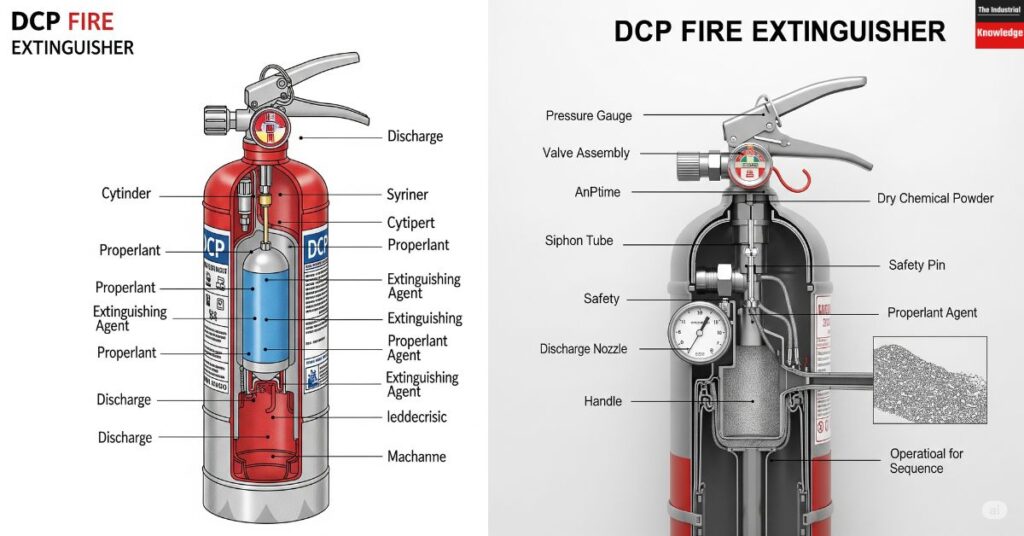
Components of a DCP Fire Extinguisher
Cylinder
The cylinder body shall be of the welded type. All ferrous fittings shall be welded to the body, while all non-ferrous fittings shall be brazed.
All welding shall be carried out using the shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) or gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) technique only. The electrode for welding shall conform to AWS/ASME classification.
All other requirements as outlined in section II of IS 2825 shall be followed.
Pressure Gauge
Show the internal pressure of the extinguisher. Green is OK, and red is not to be used.
Safety Valve
All DCP extinguishers shall be provided with a safety valve, preferably located on their top dished end, to meet the requirements of IS 2825. Set pressure shall be kg/sq. cm.
Hose
A flexible rubber or plastic hose or nozzle through which the powder is released toward the fire.
The length of the discharge hose shall be as specified in IS 2171 and IS 10658. The hose’s length is designed to withstand the design pressure of the DCP cylinder.
Safety Pin and Handle
Must be pulled before use. prevent accidental releases.
Operating Lever and Trigger
A hand-operated lever or trigger to activate the extinguisher and release the powder.
Label and instruction
Provides information such as the type of fire-suitable instruction for use and safety precautions.
Advantages of DCP Fire Extinguishers
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Multi-fire class use | Effective in Class A, Class B, and Class C |
| Non-conductive | Safe to use on electrical fires because this powder is non-conductive. |
| Fast and effective | Quickly breaks the chemical chain reaction |
| Cost effective | Cheaper than CO₂ extinguishers |
| Low maintenance | simple design and long shelf life |
| Work in cold weather | This powder doesn’t freeze in cold climates. |
| Stored pressure type is available | Easy to operate and one-touch release. |
| No freezing | This powder doesn’t freeze in a cold climates. |
How to Use a DCP Fire Extinguisher (PASS Technique)

Inspection and Maintenance
Regular inspection of fire extinguishers is critical for workplace safety, car safety, office safety, and home safety.
Monthly Visual Inspection
- Check pressure gauge: the middle should be shown in the green zone.
- Nozzle: free from cracks, blockages, and damage.
- Body: Check for dents, leakage, and rust.
- Safety pin: inspect proper fitting.
- Proper mounting: The extinguisher should be accessible and wall-mounted securely.
- Inspection tag: mark the date and the signature of the inspection tag.
Annual Servicing
- If required, discharge and test the extinguisher.
- Cleaning the inside of the cylinder
- Checking the condition of the powder
- Inspection of internal parts like the dip tube, valve, and O-rings. Refilling (if powder is degraded or partially used)
- Re-pressurizing with dry nitrogen
- Updating the maintenance record/tag
Applications of DCP Fire Extinguishers
- Utilized in factories, chemical plants, and warehouses where there are flammable liquids, solids, and gases.
- Best suited for Class B fires of flammable liquids such as petrol, diesel, and solvents.
- Non-conductive DCP extinguishers can easily tackle electrical fires (Class C).
- Utilized in kitchens, garages, or in areas where LPG cylinders pose risks for Class A, B, and C fire protection.
- Prevalent in buses, trucks, and automobiles to safeguard against engine or fuel fires.
- Mounted in common areas, electrical rooms, and data centers for multi-class fire protection.
- Retained as part of compulsory firefighting apparatus in buildings and public spaces.
- Good at controlling fires from welding machines, oils, fuels, and electrical origins.
- Guard areas where chemicals, paints, and flammable liquids are kept.
- Applied in mechanical, electrical, or generator zones, though not advisable near sensitive medical equipment because of powder residue.
12. Conclusion
The DCP (Dry Chemical Powder) fire extinguisher is a versatile and cost-effective fire safety tool widely used in homes, industries, vehicles, and public places. It is effective in extinguishing Class A, B, and C fires, making it suitable for combustibles, flammable liquids, and gas fires. Its non-conductive powder makes it safe for electrical equipment, though care must be taken to avoid residue damage. With features like quick operation, low maintenance, and wide availability, DCP extinguishers play a vital role in emergency fire response. Regular inspection, timely refilling, and proper training ensure their reliability during fire emergencies.
Q&A
1. What is a DCP fire extinguisher?
Ans: A DCP (Dry Chemical Powder) fire extinguisher is a fire extinguishing device that releases a dry powder to stop the chemical reaction of fire. It is effective for Class A, B, and C fires.
2. What kinds of fire can DCP extinguishers be applied to?
Ans: DCP extinguishers can be applied to:
Class A: Solid combustibles (wood, cloth, paper)
Class B: Flammable liquids (petrol, diesel, solvents)
Class C: Flammable gases (LPG, propane)
3. What is the full form of DCP?
Ans: DCP stands for Dry Chemical Powder.
4 . What chemicals are used in DCP extinguishers?
Ans: Common powders include:
Monoammonium Phosphate (ABC type)
Sodium Bicarbonate (BC type)
Potassium Bicarbonate (BC type)
Urea-based Potassium Bicarbonate
5. What is the color code of a DCP extinguisher in India?
Ans: IS 2190 specifies that the DCP fire extinguisher contains a blue band on the red cylinder.
6. Are DCP extinguishers suitable for electrical fires?
Ans: Yes, DCP extinguishers are non-conductive and can be used safely against electrical fires (Class C). However, powder residue could ruin sensitive electronics.
7. How does a DCP extinguisher function?
Ans: Upon activation, it releases a pressurized dry powder (typically CO₂ or nitrogen) that extinguishes the fire by smothering, depriving it of oxygen, and breaking the chemical chain reaction.
8. How to operate a DCP fire extinguisher?
Ans: Apply the PASS method:
P – Pull the pin
A – Point towards the base of the fire
S – Squeeze the handle
S – Sweep from side to side
Leaves a powder residue that’s hard to remove
9. What are the disadvantages of DCP extinguishers?
Ans:
Not for Class D (metal fires) or Class K (kitchen oil fires)
Harms sensitive equipment because of dust
10. Where are DCP extinguishers used?
Ans:
Factories and industries
Petrol pumps and workshops
Residential homes, offices, and automobiles
Electrical rooms and data centers
Public facilities and hospitals (non-critical zones)
