Reactor Jackets Explained Types, Benefits, and Uses
What are reactor jackets ?
A jacketed vessel is a container that is designed for controlling Temperature of its contents, by using a cooling or heating “jacket” around the vessel through which a cooling or heating fluid is circulated.
Jacket is a cavity external to the vessel that permits the uniform exchange of heat between the fluid circulating in it and the walls of the vessel. There are several types of jackets, depending on the design.
Importance in industrial applications
- Chemical reactions may proceed smoothly by being carried at the right temperatures with the assistance of the jacket.
- Jackets increase efficiency this is energy-saving and high productivity.
- A reactor jacket keeps temperatures stable enough for pharmaceutical industries and food processors to produce the quality and stable products.
- Their applications are multiple jackets keep a reactor both warm and cold.
- They prevent overheating or sudden temperature changes and thereby reduce risks in processes involving heat-sensitive reactions.
- Cost Savings : They improve energy use and minimize waste, hence reducing cost of running.
- The performance of these jacket can be defined by 3 parameters : 1.Response time 2.Uniformity of jacket temperature 3.Stability of jacket temperature
Working of Reactor Jackets
Reactor jackets are an adjustment method to control the temperature of a reactor vessel by wrapping a layer or system around a reactor that can be heated or cooled. Here is the basic principle of how they work:
Circulation :
This is a heating or cooling medium, whether it is water, steam, or oil flowing through the jacket surrounding the reactor.
Heat transfer :
The heat is transferred either to or away from the reactor’s contents, according to whether it needs heating or cooling.
Temperature control :Sensors in the reactor monitor temperature the system modulates flow of the medium to maintain the desired temperatures.
Even temperature heating or cooling :
The designing distributes the temperature throughout the reactor evenly, thereby ensuring uniformity as the characteristic of the result.
Types of Reactor Jackets
- Conventional type jacket
- Half pipe coiled jackets
- Dimple jackets
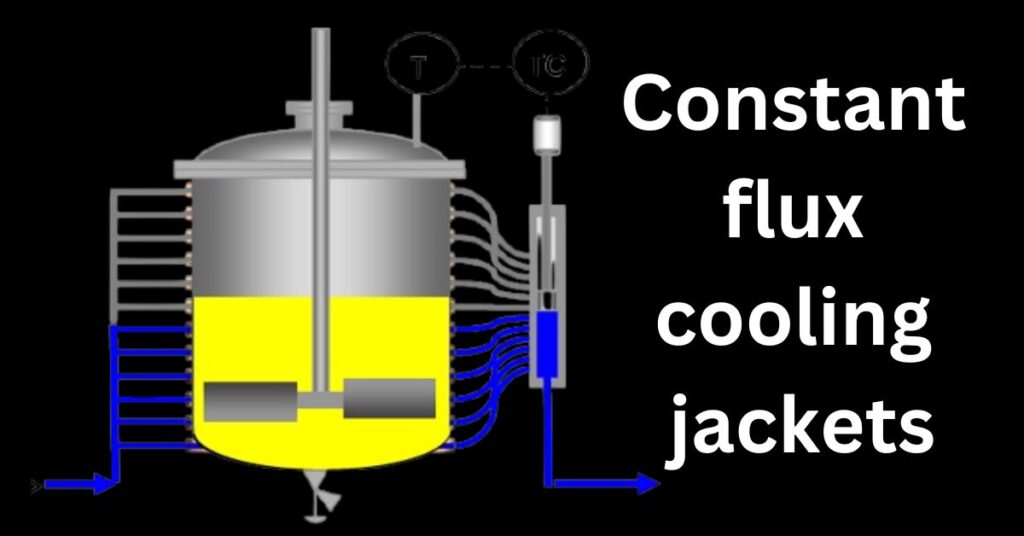
- Constant flux cooling jackets
- Internal coil jacket




1. Conventional Type Jacket

A conventional type jacket is among the simplest constructions applied for warming or cooling vessel reactors. As such, the inner constituent component is not seen and it therefore is relatively easily erected, however not so for effective heat transfer.
- A simple conventional jacket having no internal constituent is very much inefficient for the purpose of heat transfer. Velocity is very low in the flow media and this will result in delivering a bad heat transfer coefficient.
- Internals consist of baffles which guide flow in a spiral.
- Temperature gradients could exist between the vessel side walls and the bottom. Traditionally, to increase performance, some jackets contain baffles that guide the flow of the heating or cooling fluid in a spiral pattern.
- If your application requires tighter temperature control and distribution, then this is not likely a good option for you.
- Used at pressures below 50 psi.
- It is typically used when there is a demand for high volume heating or cooling fluids.
- Design leads to low pressure drop thus energy saving in certain applications.
Applications
Low-critical process applications that do not require tight temperature control. Low-pressure applications involving large fluid quantities such as a simple chemical process or heating application.
Advantages
- Less expensive due to its very minimal design.
- Installation and maintenance are also easy.
- It is used for basic applications where the condition for temperature does not have to be strict.
2. Half Pipe Coiled Jackets

Another term for a half-pipe coiled jacket is a split-coil jacket. It is employed for heating and cooling reactor vessels in an effective manner. The half-pipe or split coil is welded around the outer surface of the vessel. Its primary usage in industries lies in its greater efficiency and superior pressure handling capacities.
- It is wound helically or spirally around the outer vessel. This pipe is used to make a passage for the heating or cooling medium.
- The coils allow flow at high velocity which causes turbulence. Thus, the process of heating or cooling becomes faster and it is enhanced with higher efficiency.
- Half-pipe coiled jackets result in greater coefficients of heat transfer than conventional jackets. The primary reason for the same is because the turbulence resulting from a greater speed will boost the coefficient of heat transfer.
- The contents within the vessel quickly warm up or cool down. Saving time as well as energy while shortening batch times in any processing procedure decreases the costs due to the cheap process.
- Halfpipe coiled jackets can withstand much higher pressures up to 450 psi than that of their equivalent traditional jackets. They are, therefore, suitable for applications in which the process involves fluids pressurized during heating or cooling.
- The process is finished almost very efficiently. This is because the heat transfer fluid drains pretty fast through the coils during the final stages of the process. This cuts down on downtime.
Limitation
- These complex designs and the installation procedure of these jackets may make installation costlier.
- Repair and maintenance might require special knowledge and tools.
Advantage
- Quick heating and cooling save energy and hence reduces operational costs.
- The short batch times lead to a higher productivity rate.
- It can safely handle high-pressure operations; hence, suitable for demanding industrial processes.
- The fast heating and cooling save energy, hence reducing the operational cost.
- Short batch times result in increased productivity.
- This system can safely handle high-pressure operations, hence making it appropriate for demanding industrial processes.
3. Dimple Jackets

Dimple jacket, therefore, refers to a specific category of the transfer jacket with maintaining the interior heat of the vessels. Some major industries involve, for instance in food, chemical, or medicines, especially under process heating cooling, chemical reacting conditions extremely of high degree accuracies require applying dimple jacket.
This shall be further strengthened by some minor weld spots bond the outside-thin-skinned vessel with outer shell along vertically and horizontal equally spaced. Sometimes, that even goes about, 50 mm on-center placement.
- These so called dimples impart turbulence to the heating or cooling media as it flows through the jacket.
- The punched or spot areas are called dimples.
- Provides large heating or cooling for virtually and shape and size of vessel.
- Its pressure drop is high.
Advantage
- Applicable to site erection where space and weight are the concerns.
- Incorporate a lesser amount of material compared to half-pipe or conventional jackets hence relatively cheap.
- Applicable to most industrial applications for pressures up to 300 psi.
Limitation
- If very high pressures are demanded, then half-pipe coiled jacket might be used
- Normally, one would design every dimple jacket as a single design for the vessel, therefore lead time is usually high.
Expand Your Knowledge on [Centrifugal Pump]
4. Constant Flux Jackets
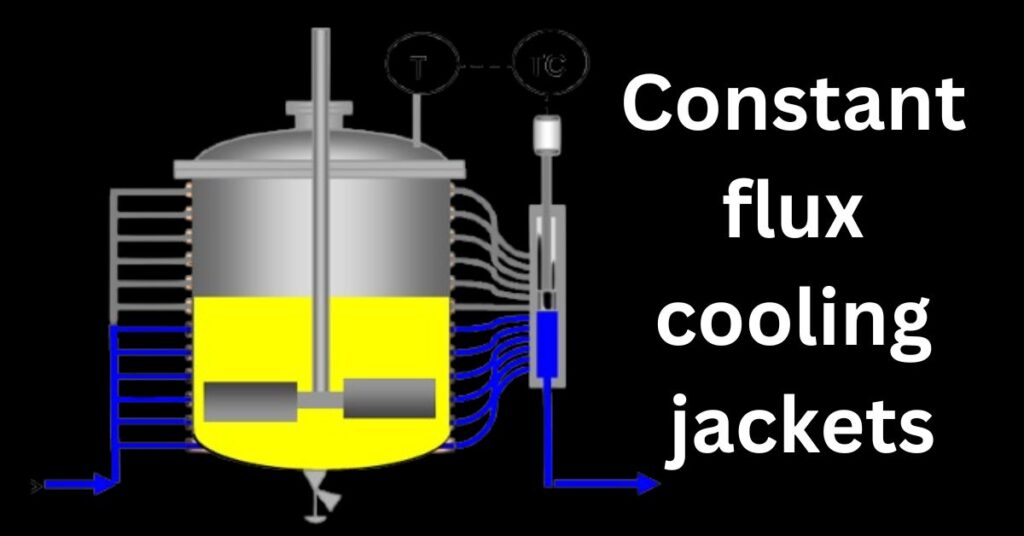
A constant flux jacket is a specialty jacket used on industrial vessels. It gives excellent and efficient temperature control. Unlike jackets designed by other methods, the constant flux jacket ensures the steady flow of the heating or cooling medium through the entire surface of the vessel. This is why constant flux jackets are used in any process where uniform temperature will be required to achieve good quality product and efficient processing.
- The constant flux cooling jacket is a relatively recent development.
- It is not a single jacket but has a series of 20 or more small jacket elements.
- The temperature control valve operates by opening and closing these channels as required.
- By varying the heat transfer area in this way, the process temperature can be regulated without altering the jacket temperature.
- The constant flux jacket has very fast temperature control response due to the short length of the flow channels and high velocity of the heat transfer fluid.
Limitation
- High-design and manufacturing can make the coats expensive than others, for instance, ordinary ones like traditional coats.
- High and precise control may demand to constantly recalibrate it to achieve top performance.
Advantage
- Constant flux coats outshine traditional and dimple coats concerning heat distribution.
- The jackets are less energy-hungry this means they tend to use less power when in operation.
- They can fit on any of vessel designs, their sizes included. They, indeed, should adjust according to any industry requirements.
5. Internal Coil Jacket

This is an inert coil jacket mounted inside a vessel instead of a conventional mounting around the outside of the vessel. Coils can rapidly heat or cool fluids in a tank by passing hot or cold mediums like water, steam, or oil through the coils. It is a very effective method for applications requiring rapid temperature change.
- Utilized inside vessel for transient heating or cooling of liquid.
- They move from top head down.
- Cleaning is an issue in this.
- They provide high flow, high internal and external pressure.
- Used in application where in non-corrosive.
- Efficient heat transfer.
- Rated up to 900 psi.
Advantage
- It is used in the processes that require the temperature of the fluid to be changed; it is therefore more efficient.
The coils are immersed in the vessel, hence no further space is needed outside like in conventional jackets or halfpipe jackets.
They can operate at a high pressure, thus high-performance application is appropriate for them.
Limitation
- It is not quite an easy process to clean coils and other interiors of the inner vessel, and significant time is devoted to that purpose.
- They are not good for such processes which are needed with frequent cleaning with food and in pharmaceuticals too.
- This was not strong enough to anything highly corrosive agents; to that chemical process, it isn’t ideal.
Reactor Jacket Safety Hazards
- Over pressure hazard
- Thermal stress
- Incompatible Material Corrosion
- Inefficient heat transfer
- Operator safety hazard
- Leakage
- Wrong PSV Install
- Improper Design Of jacket
- Overload of capacity
Reactor Jacket Chocking and leakage Problem
How to detect Reactor jacket are leakage
- Perform routine checking on welding joint, flanges, and fittings to detect early signs of wear or corrosion.
- ensure a pressure sensors and transmitter are working condition and operate safe limits and avoid overpressure situations.
- use compatible utility in reactor jacket.
Chocking problem in reactor jacket
- Install filter/ strainer provide in utility line to prevent choking problem.
- Install pressure sensor in line to detect abnormal flow.
Expand Your Knowledge on [Glass Lined Reactor]
Conclusion
This would be a jacket of a particular industrial process reaction. It does help in properly controlling the temperatures, effectively transferring heat, and maintaining the stability of a given process. Due to that, knowledge on the various jackets, how they work, and the advantages which they give the industry makes the choice accessible.
Proper design, maintenance, and routine inspection will have to conquer overpressure, thermal stress, leakage, and material incompatibility. Filtration for the prevention of chocking and the use of compatible utilities enhance the efficiency and safety of operation.
Best practice and removal of probable hazards make reactor jackets important in optimizing process efficiency and cost-effectiveness and industrial safety.

Excelent post!!! Could you send this paper for me?